According to population and area, Colorado is the 8th-largest state in the United States. It is well-known for its stunning scenery, which is accompanied by a wealth of wildlife. The Rocky Mountain bighorn sheep is Colorado’s official state animal. Until 1931, the lark bunting was the official bird of Colorado. These birds, which are native to Colorado, were chosen for their courtship dance and melodious singing. It is a member of the American sparrow family, the lark bunting.
About Lark Buntings

These buntings can be easily distinguished by their distinctive male behavior. They measure about 15 centimeters in length (6 inches). In the summer, the ladies tend to be smaller and less showy than the males. Lark buntings are medium-sized songbirds that belong to the sparrow family. Buntings of the lark family have short, white-tipped bills and short, white-tipped tails. A huge white patch can be seen on their wings. There are two distinct types of male lark buntings: those that mate during the breeding season, which have dark bodies with white wings, and those that don’t.
Males become mostly brown in the winter. Among other things, they have brown backs, heads, and wings. In contrast, the white or light brown chests and underparts of these birds are striking. Black or dark brown streaks can be noticed frequently on their backs. The wings may also have a white spot on them. In the winter, the female Colorado state bird resembles the male quite closely. Similarly, immature males are brown with dark streaks in their fur. It’s common for hatchlings to have a fluffy grey down coat.
Also, know What is the State Bird of Mississippi?
Why is the lark bunting the state bird for Colorado?

The wild lark bunting was chosen as the state bird of Colorado, despite the fact that the bird is neither a lark nor a bunting. In fact, it’s a sparrow. The singing of the local bird and its acrobatic courtship dance endeared it to the people of the state. Residents are enthralled by the male sparrow’s scintillating dance as he tries to woo a beautiful female sparrow. Singing to his potential partner, the male propels himself into the air and spins down while doing so.
When did the lark bunting become the state bird for Colorado?
Legislators in the state of Colorado debated in 1931 about which bird should be designated as the official emblem of the state of Colorado. Most states, like Colorado, hold a student ballot. The meadowlark, mountain bluebird, and lark bunting were the three finalists in the competition instead of accepting the decision. There are many other states that have the same state bird as Colorado, and the state wanted to stand apart. Even though the birds can only be found on the Eastern Plains of the state, the state still had high hopes for this little sparrow.
Diet of Lark Buntings

Except for when they’re nesting, lark buntings feed in large groups. On the ground, they tend to scavenge for food. Insects such as grasshoppers, beetles, bees, and ants are all that they eat during the summer. They eat seeds from grasses and weeds throughout the winter. It is true that lark buntings are omnivores, however, they prefer bugs over weed seeds in their diet. Meat accounts for two-thirds of its diet in the summer, when insects are plentiful.
In the case of lark bunting babies, they eat nothing but meat. While foraging, they remove seeds from grasses or tap the ground to find seeds. They stalk and chase their prey when they are hunting insects. Both sexes will pursue fleeing prey in flight, but females are more likely to do so. Females are also more agile on the ground when searching for food.
How do these birds act?

These friendly avians, according to Langdon, have a gentle demeanor. They favor sagebrush as a habitat in grasslands and plains. They make their nests on the ground and tuck them away under plants. Grassy places are a good place for the lark bunting to set its shop. In contrast to other birds’ nests, theirs is shaped like a deep cup.
Winter is a time of migration for the lark bunting. Even though it calls Colorado home, the state can be too cold for the birds, as it is for many human snowbirds. Arizona, Texas, and northern Mexico are among the places where it gets cold in the winter.
There are two unique songs sung by lark buntings, as well as other communication sounds. Spring and summer are prime times for men to perform these two songs in order to attract a partner. They have a slow, distinct melody and a trill in their singing that distinguishes them from other birds. At the most, they’re just eight seconds long. As they return to the nest, their bird cries include an in-flight sound, a call to notify their mate and their young, and a hungry bird sound.
Habitat of Lark Buntings

All across the central and western United States, lark buntings have made their home. Meadows and sagebrush-covered areas are their summer habitats. On the ground in grassy places and under shrubs, lark buntings build their nests. In shape, the nests resemble an open cup with deep sloping rims; Eggs are laid in batches of two to six. During the colder months of the year, large numbers of them go north to the deserts of Texas, Arizona, and northern Mexico.
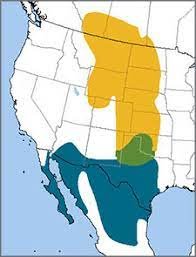
Where can you find Lark Buntings?
The state bird of Colorado often lays its eggs on the ground. Often, they’ll be buried in the ground under bushes. In addition, lark buntings are often found foraging on the ground. It is common for them to eat insects during the summer months, but they also eat seeds. These birds are not uncommon to swoop down and snatch insects in mid-flight.
The Colorado state bird, the Prairie Warbler, can be found on plains across the Midwest during the summer. It’s also possible to find them in Canada’s southern regions. Large flocks of Colorado’s state birds will migrate south in the fall. The bird will spend the winter in Mexico before making its annual spring migration back to its nesting grounds.





